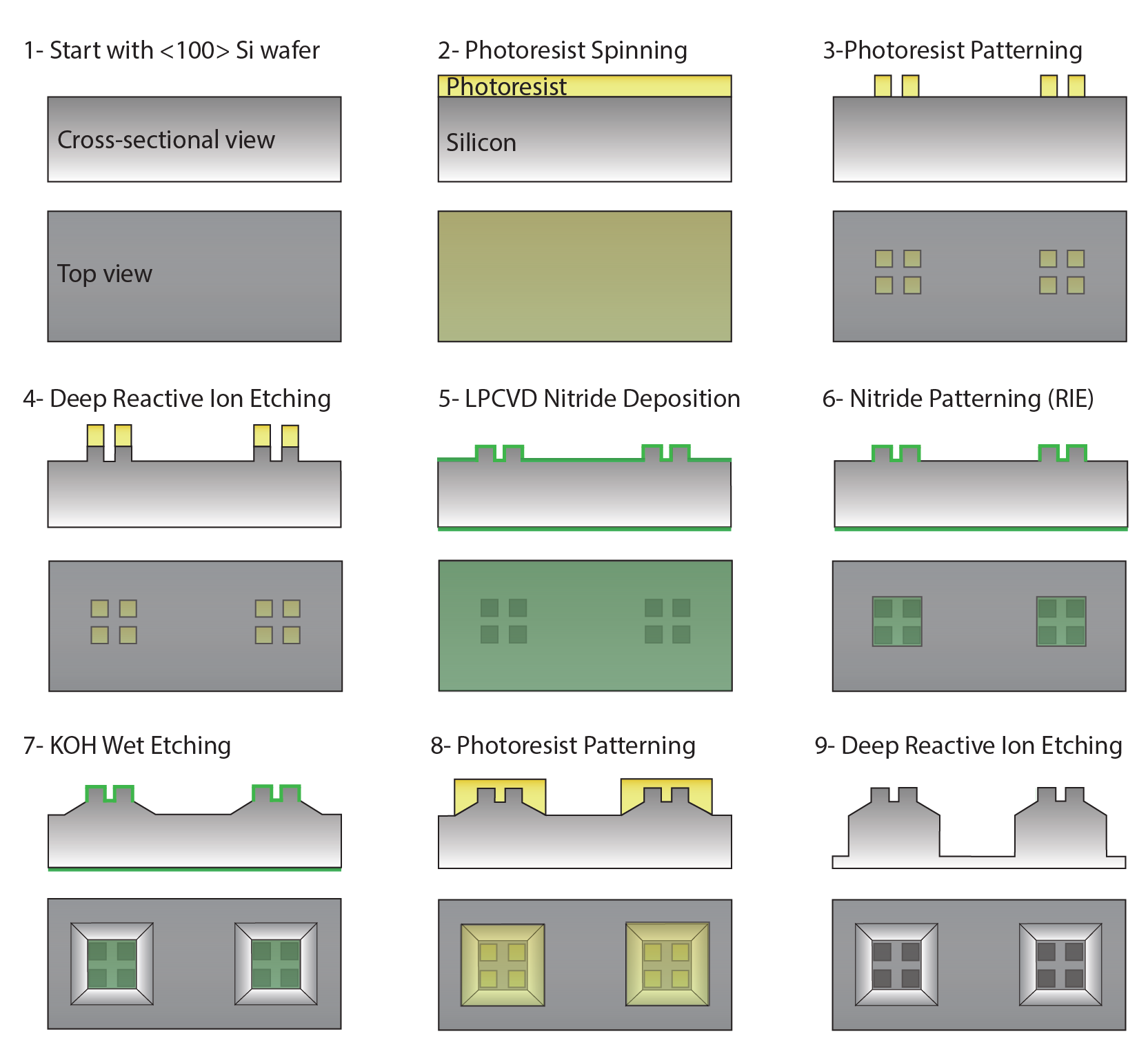
一种基于网状微孔高通量无标签分离CTC簇的方法。
Introduction
思路:
- 在单个CTC之外,CTC簇具有重大的科学和临床意义。尽管CTC簇极为罕见(仅占所有CTC的2—5%),但它们的转移倾向比单个CTC高一百倍。此外也发现了CTC簇中包含免疫细胞,突出了其在阐明肿瘤-免疫系统相互作用及其在转移中的作用方面的效用。因此需要增加对CTC簇的研究。
迄今为止CTC簇的有效分离受到限制,因为CTC分离技术的灵敏度和特异性主要针对单细胞检测进行校准。
- 微滤技术因其快速和直接的操作而被广泛用作CTC检测 。然而在生理压力下CTC簇可以将自身重组为单列链状结构,并穿过小至 5 μm的束隘,表明在过滤中使用更高的压力时,CTC簇很可能通过过滤孔。此外微滤过程中经历的更高剪切力可能会损坏CTC簇或将它们分解成单个细胞,从而破坏有效富集。
- 长期以来用于分离单个CTC的基于抗体的富集系统由于依赖于特定的膜抗原,因此只能检测异质性CTC群体中的CTC簇的特定亚群。此外,CTC簇的较小表面积与体积比对基于抗体的技术的免疫捕获效率产生负面影响,使其在CTC簇富集方面特别低效。
- 专门针对CTC簇的微流控芯片可以实现相对更高的灵敏度。然而它们要么以临床上不可行的处理速率 ,要么由于狭窄通道中的高流速而使簇损伤,尤其是多达数十个肿瘤细胞的大型簇。
作者开发了Cluster-Wells,可以高灵敏度、高通量地从未处理的全血样本中温和地分离出大大小小的CTC簇,而无需靶向肿瘤特异性抗原,并在亚生理流速下保持其完整性。
Design and microfabrication of the Cluster-Wells
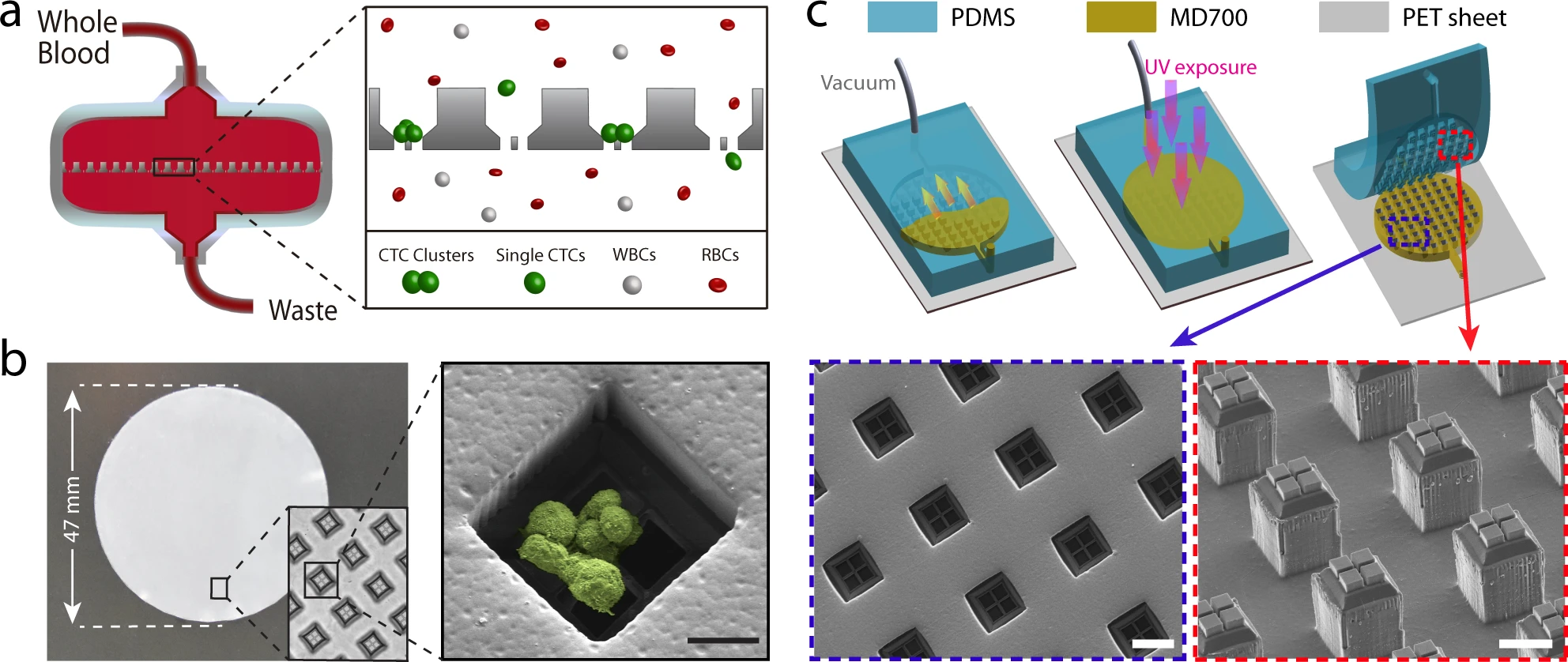
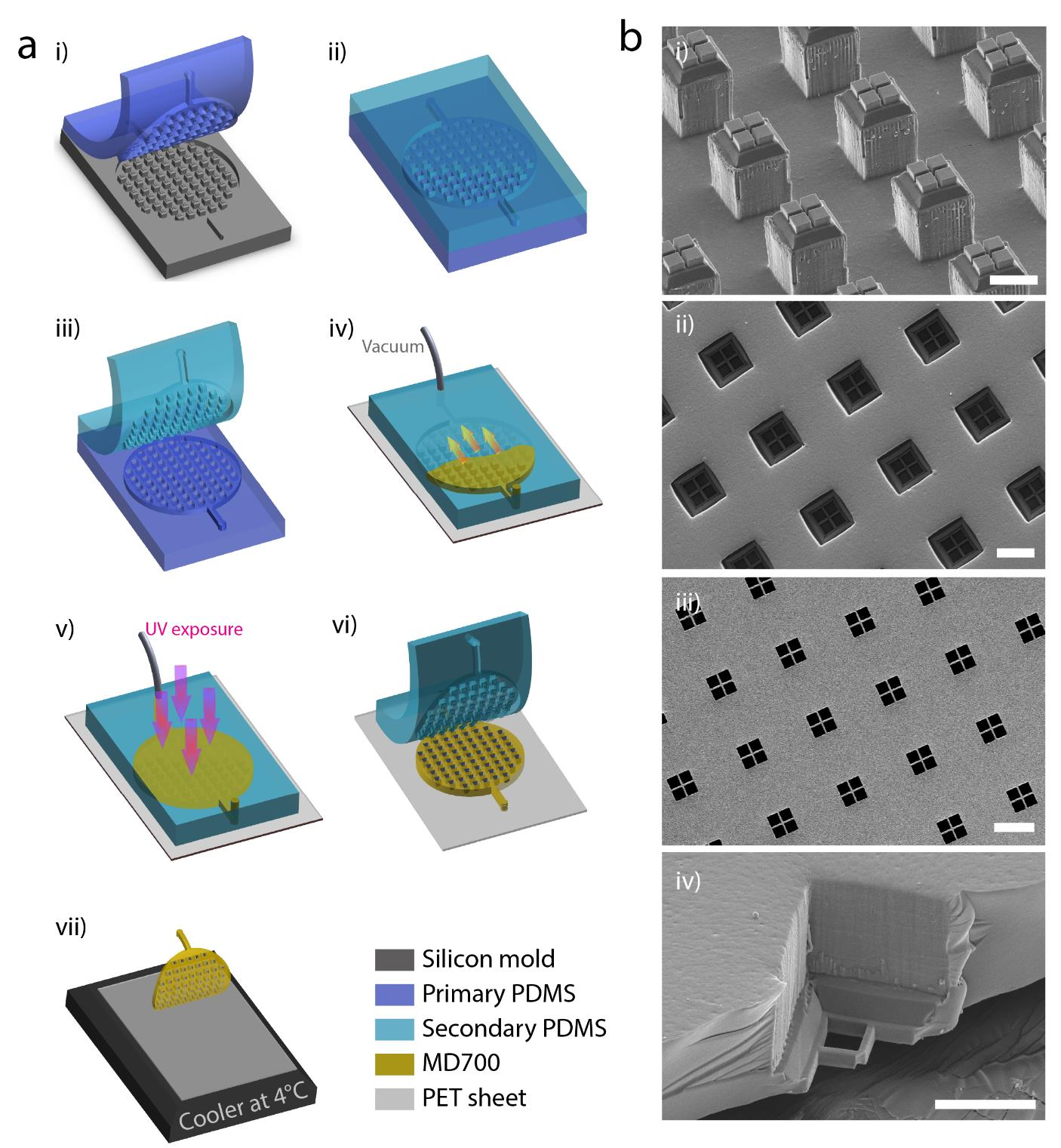
- (a)Cluster-Wells工作原理示意图。每个微孔都包含一个网状开口(开口直径为15 μm × 15 μm),旨在保留细胞簇而又不影响血液中的单个细胞通过。微孔侧壁倾斜,可以限制CTC簇的重定向,也能减少细胞所受横向应力。
- (b)以47 mm直径膜形式制造的Cluster-Wells照片,可用于商业过滤器支架。插图显示了设计用于捕获CTC簇的单个孔及一个孔捕获的血液中人前列腺癌细胞(LNCaP)簇的扫描电子显微照片。
- (c)Cluster-Wells制造过程示意图。参考辅助材料,先用硅片制造负模,通过2次PDMS浇铸,将图案转移到PDMS模具上。然后使用光聚合物Fluorolink MD700(该材料具有抗细胞粘附能力)填充,最终得到成品膜。
辅助材料:
Device characterization and optimization using simulated blood samples
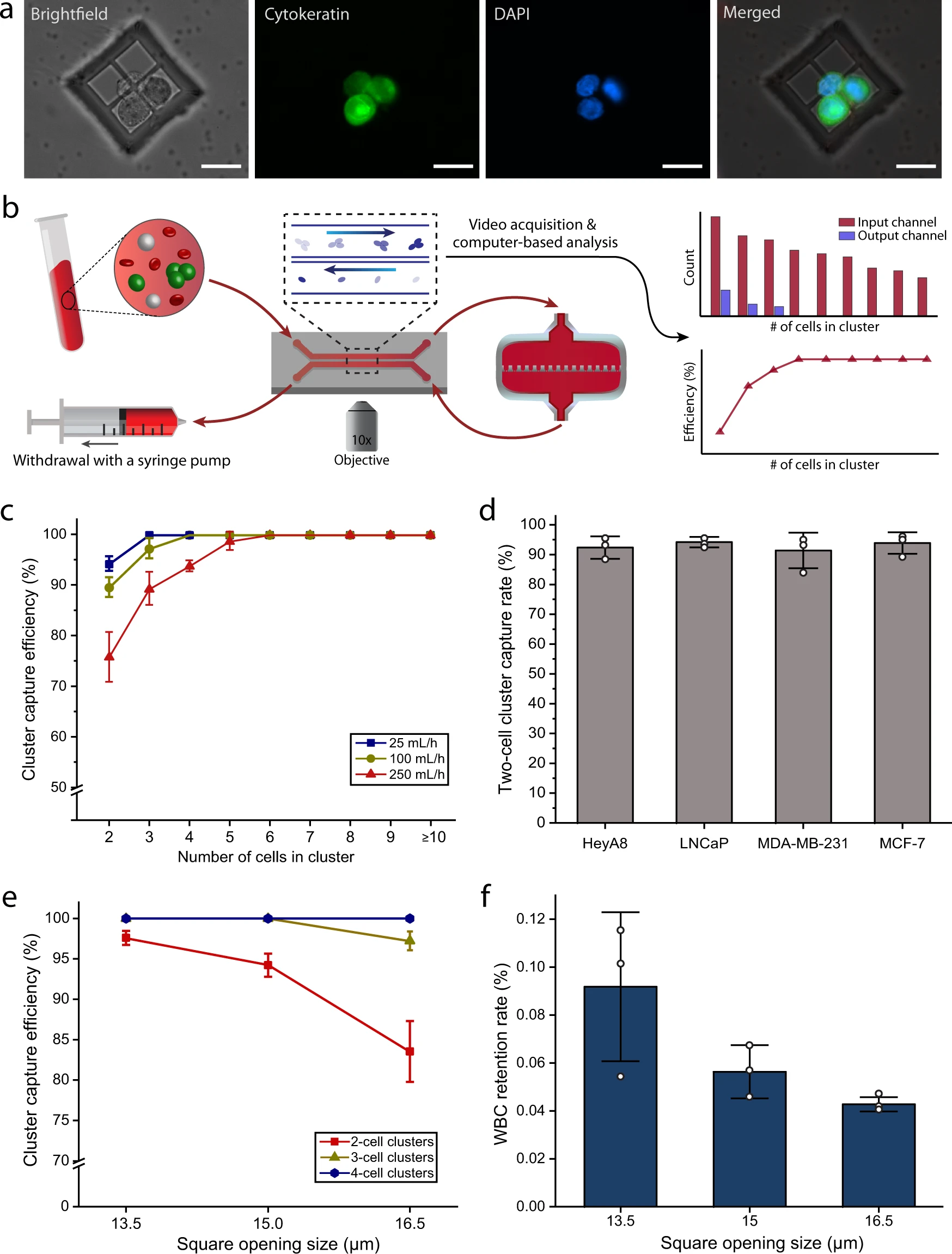
- (a)捕获的全血中LNCaP簇的代表性白光/荧光图像。包括细胞角蛋白(绿色)和细胞核(蓝色)。
- (b)用于表征研究的实验装置的示意图。使用双通道微流控芯片对进入和离开Cluster-Wells的细胞进行目视跟踪和计数,以计算捕获效率。
- (c)Hoechst 33342标记的LNCaP簇在不同流速下的捕获效率。
- (d)流速为25 mL/h时,前列腺(LNCaP)、乳腺(MDA-MB-231&MCF-7)和卵巢(HeyA8)癌细胞簇的双细胞簇捕获率。由于Cluster-Wells仅依赖于簇的物理属性,可以有效地捕获了不同肿瘤类型的簇,而与它们的表面抗原无关。
- (e)流速为25 mL/h时,不同尺寸开口的2个、3个和4个细胞的LNCaP簇捕获效率。
- (f)处理一管(10 mL)全血后,不同尺寸开口的白细胞(WBC)保留率。综合特异性和敏感性的考量,选择了15 μm的参数。
Cluster retrieval from the Cluster-Wells
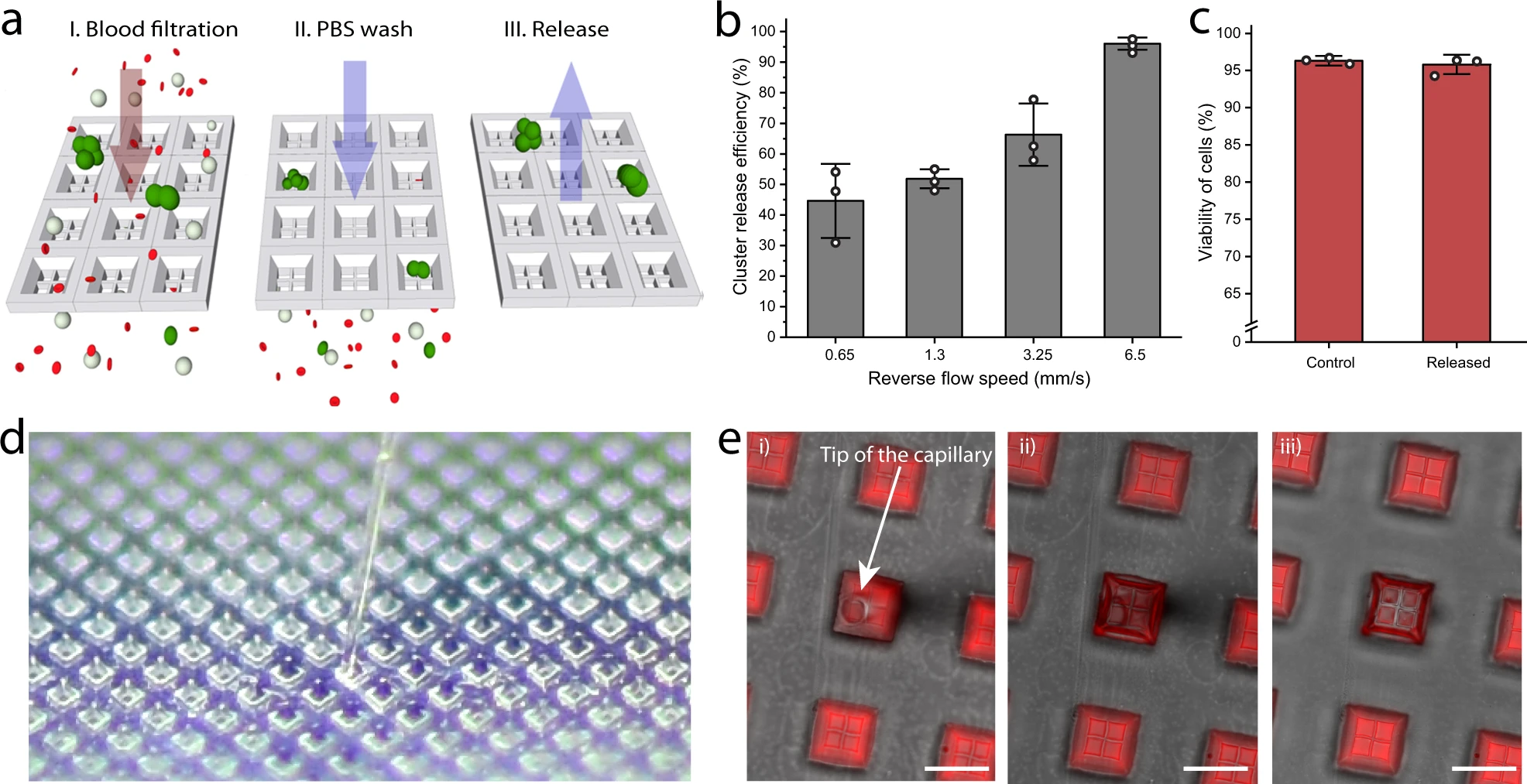
- (a)释放过程的展示。上图显示了将LNCaP簇加入全血中并使用Cluster-Wells进行处理、PBS 洗涤和应用逆流将捕获的簇释放到培养皿中的过程。
- (b)装置在不同逆流速度下的释放效率。在逆流速度~6.5 mm/s(100 倍捕获流速)时,几乎所有(约 96%)的簇都可以成功回收。
- (c)在培养皿内对回收的细胞(经过~6.5 mm/s逆流速度)进行活力测定,其平均活力(~95.8%)与对照组没有显著差异,表明该装置及释放方案都没有对细胞活力产生显著影响。
- (d)Cluster-Wells和单个微孔内显微操作的照片。
- (e)Cluster-Wells从过滤支架上取下后的荧光显微镜图像。由于表面张力作用,先前引入的荧光染料溶液留在孔内,不会因为重力泄露。没有操作的情况下,微孔在约10 min内干燥。
Isolation of CTC clusters from patient samples
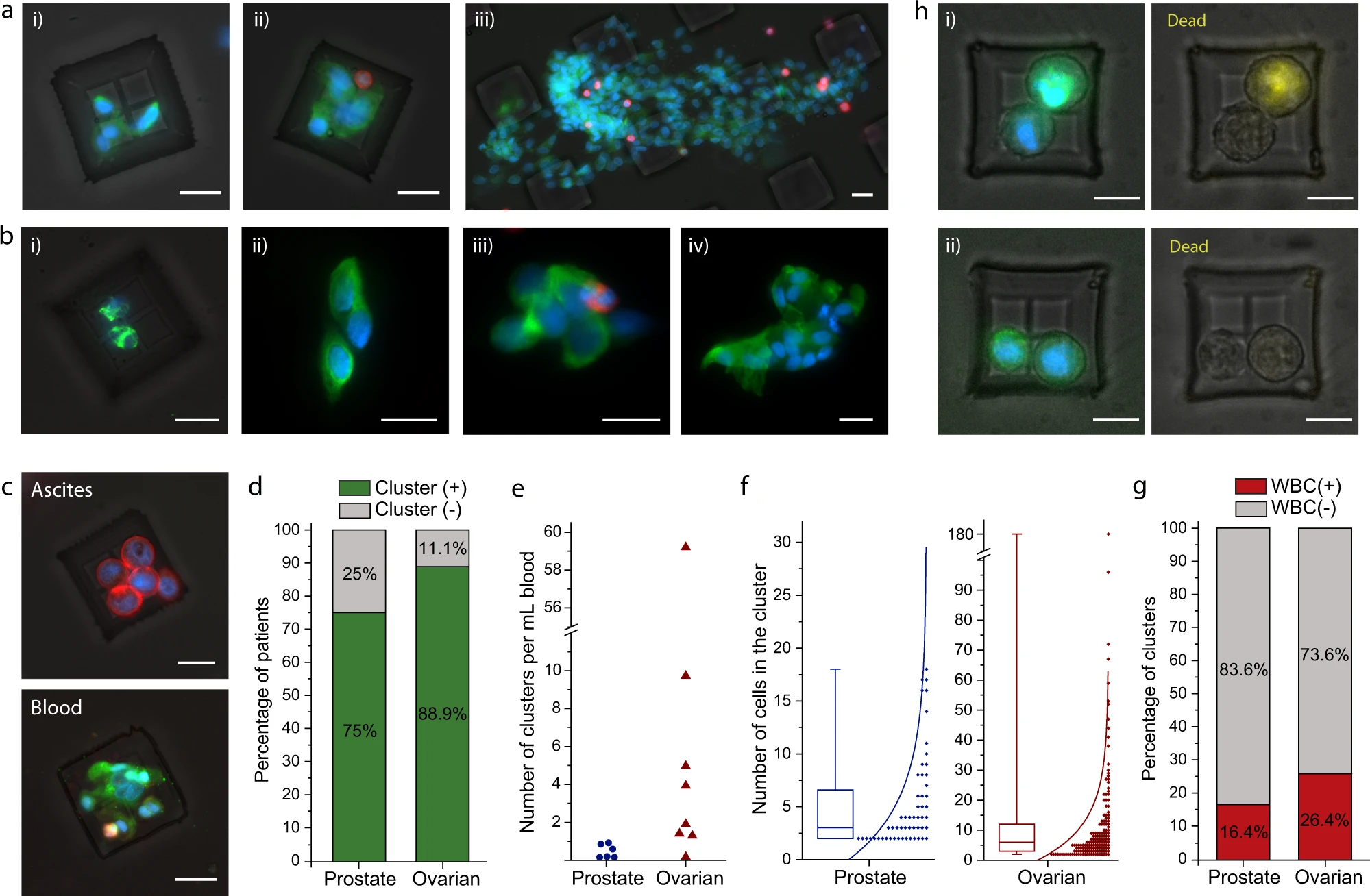
- (a)从卵巢癌患者中分离出的CTC簇的荧光显微镜图像。捕获的细胞用细胞角蛋白、波形蛋白(绿色)、CD45(红色)和 细胞核(蓝色)染色。其中iii为多达150个细胞的簇,这一尺寸如果通过微流控芯片极有可能堵塞或者使其分散。
- (b)从转移性前列腺癌患者中分离的CTC簇的图像。捕获的细胞用细胞角蛋白、波形蛋白、PSA/KLK3、EpCAM(绿色)、CD45(红色)和细胞核(蓝色)染色。
- (c)同一时间点,从卵巢癌患者的腹腔抽取的外周血中分离的簇和腹水样本中分离出的肿瘤球。血液中分离的CTC簇在形态上与腹水中分离的肿瘤球有所不同。腹水样本中的肿瘤球固定并将细胞角蛋白、EpCAM(红色)、CD45(绿色)和细胞核(蓝色)染色;从血液样本中分离的CTC簇固定并将细胞角蛋白、波形蛋白(绿色)、CD45(红色)和细胞核(蓝色)染色。
- (d)血液样本中含有CTC簇的前列腺癌和卵巢癌患者的百分比。
- (e)每毫升前列腺癌和卵巢癌患者血液样本中观察到的CTC簇数。患者之间检测到的CTC簇的数量差异很大。
- (f)在前列腺癌和卵巢癌CTC簇中观察到的细胞数量分布。相比而言,卵巢癌CTC簇由比前列腺癌CTC簇具有更多的肿瘤细胞组成。
- (g)不同癌症类型的纯CTC簇和白细胞相关CTC簇的百分比。
- (h)从卵巢癌患者中分离出来的CTC簇的图像,并进行了基于荧光的活力测定。图像显示了由(i)活细胞和死细胞(黄色)以及 (ii)仅由活细胞组成的CTC簇。
Molecular analysis of patient CTC clusters
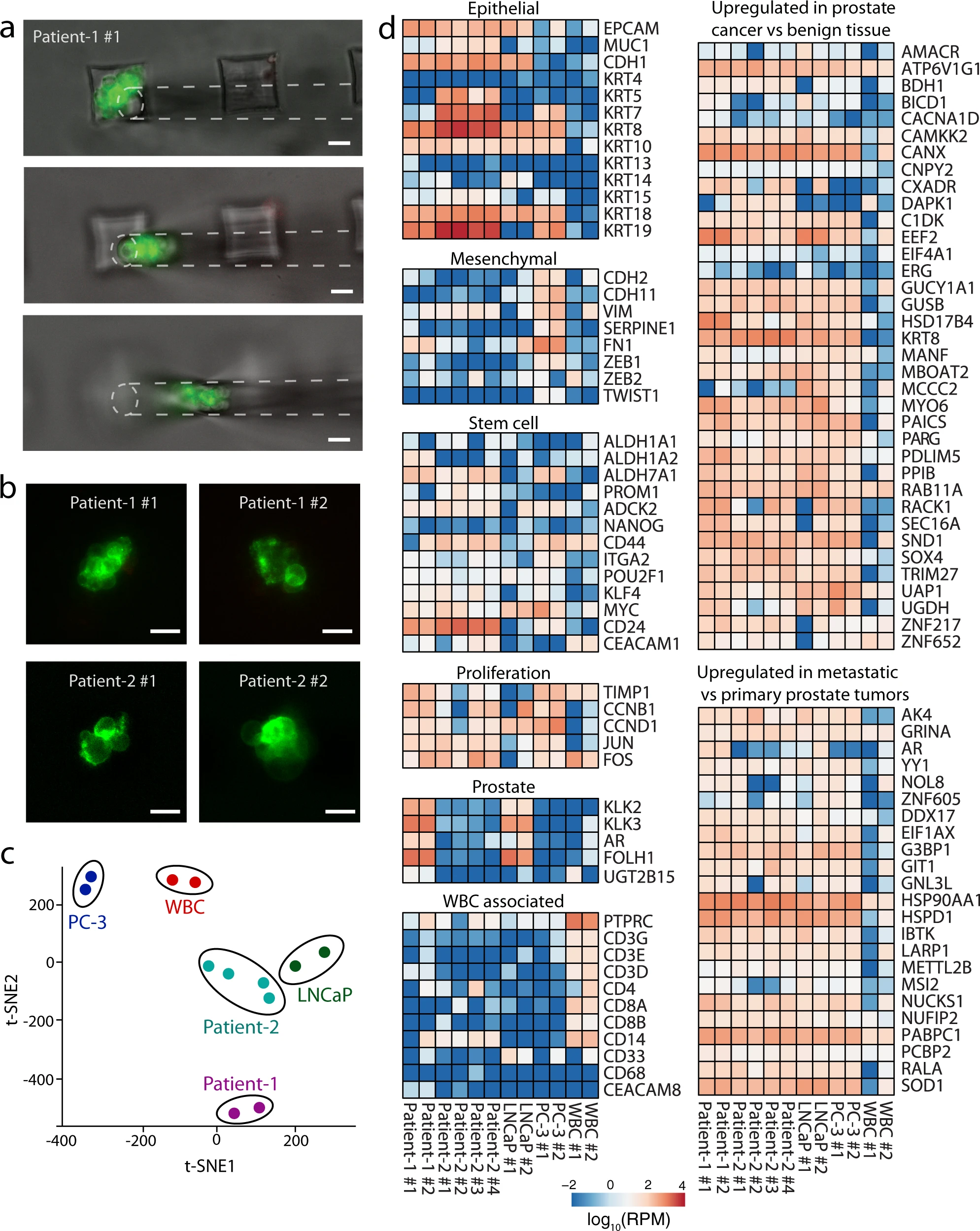
- (a)从转移性前列腺癌患者(Patient-1)的血液样本中分离出的CTC簇的显微操作。在血液过滤和PBS洗涤之后,使用FITC缀合的抗EpCAM和前列腺特异性膜抗原(prostate specific membrane antigen,PSMA)抗体在设备上对分离的可行CTC簇进行染色,使用荧光显微镜进行扫描,并直接从设备进行显微操作。
- (b)接受RNA-Seq的前列腺CTC簇的代表性荧光显微镜图像。图像是在从设备中取出用于分析之前拍摄的。
- (c)已测序的患者、前列腺癌细胞系和白细胞的t分布随机邻近嵌入(t-SNE)图。观察到来自同一患者的不同簇或细胞系倾向于聚集在一起。
- (d)热图显示来自两名转移性前列腺癌患者、前列腺癌细胞系和白细胞的分离CTC簇中选定基因的表达水平。
Discussion
- 作者介绍了一种可以选择性地分离癌症患者全血样本中的CTC簇的方法——Cluster-Wells。其优势在于:
- 大量、并行且基于生理性流速,不会破坏CTC簇的结构完整性;
- 微孔陷阱的形式可以高灵敏度捕获,且具备独立性;
- 微孔陷阱结构而不是滤网可以减少细胞所受外部压力,以保持活力可用于下游分析;
- 与商用滤器支架兼容,易于集成到基础研究或临床工作流程中。
Reference
Boya M, Ozkaya-Ahmadov T, Swain B E, et al. High throughput, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cell clusters in meshed microwells: 1[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 3385.